SciTech #ScienceSunday Digest – 50/2016.
Permalink here: http://www.scitechdigest.net/2016/12/scitech-digest-502016-1.html
Equation for intelligence, Faces diagnose diseases, Deep learning everywhere, CRISPR inhibitors, Direct neural implants, Artificial blood nanoparticles, Zero-g experiments via drones, Ultrasound microbubbles open brain, Nanocrystal night vision, Energy technologies.
1. An Equation for Intelligence
A new theory of connectivity based on the equation N = 2^i – 1 attempts to describe very simply how neurons and their networks flexible assemble to gather knowledge and reason about concepts, in short how intelligence works https://singularityhub.com/2016/12/07/this-one-equation-may-be-the-root-of-intelligence/. Not only does the theory question the dogma of “cells that fire together, wire together” but many animal experiments show the equation at work many different brain regions that control key functions including feeding, behaviour, and fear. Basically core wiring is innately determined by genetics, with clusters or cliques of networks being combined to represent ever more greater conceptual complexity. We can expect this to be tested sooner rather than later in deep learning and neuromorphic chip applications.
2. Predicting Diseases from Facial Features
Dysmorphology, the practice of diagnosing disease by observing a patient’s features, exploits the fact that many genetic conditions have associated effects on face development – and new facial recognition software called Face2Gene automates this process, comparing features across a vast database to approach human expert level diagnoses https://www.technologyreview.com/s/603038/diagnosing-disease-with-a-snapshot/. Of 7,000 genetic syndromes, Face2Gene estimates that half have distinct facial patterns, and any tool that accelerates diagnoses to allow more rapid interventions will be a boon for patients and payers. This work relates to that from a couple of weeks ago in which, controversially, facial features were used to predict criminality.
3. Deep Learning is Everywhere
First, a new deep learning system is being used to create vastly improved hearing aids able to extract speech and other important sounds from chaotic background noise, and in tests people’s ability to understand words from background noise was boosted from 10% to 90% http://spectrum.ieee.org/consumer-electronics/audiovideo/deep-learning-reinvents-the-hearing-aid. Second, a new system that correlates descriptive speech with images could provide a fully automated speech recognition capability http://news.mit.edu/2016/recorded-speech-images-automated-speech-recognition-1206. Finally, another deep learning system can turn a single photo of a person’s face into a realistic 3D model and face render http://gizmodo.com/neural-networks-can-now-turn-a-single-photo-into-a-cree-1789786327.
4. CRISPR Inhibitors & iPSCs
Further boosting the safety and utility of the CRISPR genome engineering tool, new discoveries of anti-CRISPR protein inhibitors that turn CRISPR off should further reduce the risk of unwanted off-site changes at unwanted times https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2016/12/161208143535.htm. Isolated from viruses, and presumably evolved as part of the bacterial-viral CRISPR arms race, the three different inhibitors can be spliced into cells to ensure cell or tissue specificity and drastically minimise off-target cuts. In related news CRISPR editing of induced pluripotent stem cells shows immense promise for therapeutic development http://www.nextbigfuture.com/2016/12/genome-editing-of-pluripotent-stem-cell.html.
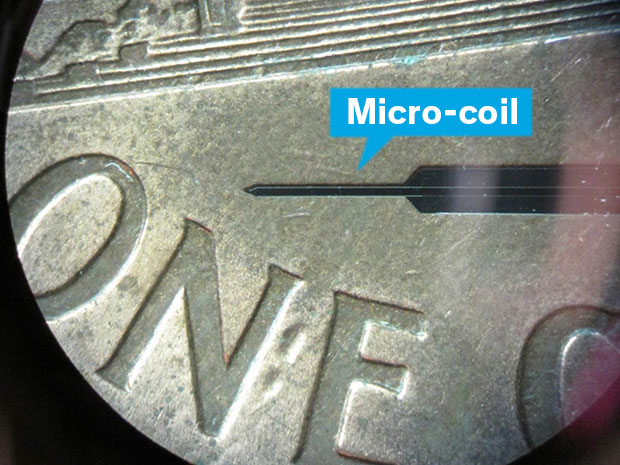
5. Direct Neural Implants & Tourniquets
Tiny microcoils measuring 100 micrometers wide and made of silicon and copper can be implanted into the brain to precisely stimulate the firing of only vertically aligned, near-by neurons via magnetic induction http://spectrum.ieee.org/the-human-os/biomedical/devices/tiny-implantable-microcoils-in-the-brain-activate-neurons-via-magnetic-fields. The benefits of this type of implant and brain stimulation are (i) not having long term performance degraded by scar tissue formation, and (ii) being able to target very specific and tiny patches of cells. Experiments in mice showed precise control of whisker movement for example. In related news a new vagus nerve interface and stimulation protocol actually stimulates platelets to better clot wounds, reducing bleeding time by 40% and blood loss by 50%, to function as a type of neural torniquet http://spectrum.ieee.org/the-human-os/biomedical/devices/neural-tourniquet-stimulates-a-nerve-to-stop-bleeding-anywhere-in-the-body.
6. Latest Artificial Blood
The latest advances with ErythroMer are showing promise as a genuine artificial synthetic blood substitute https://www.fightaging.org/archives/2016/12/erythromer-as-a-step-forward-in-artificial-blood/. ErythroMer uses synthetic nanoparticles to accomplish the functions of red blood cells, and freeze dried, stored, and reconstituted with water prior to use. The nanoparticles are about one fifth the size of a red blood cell and incorporate materials with pH dependent oxygen absorption ability that comes within 10% of normal red blood cell function. In animal tests ErythroMer performed indistinguishably from normal blood, and also resuscitated animals in shock after 40% blood loss. They’ll need chemistry for physiologically comparable carbon dioxide absorption and release before they can claim version 1.0 respirocytes however.
7. Cheaper Zero-G Experiments with Drones
A new autonomous quadcopter platform provides zero-gravity conditions for short periods of time to enable certain types of experiments to be conducted cheaper, quicker, and easier https://www.technologyreview.com/s/603037/robotic-quadcopters-could-offer-zero-g-flights-on-the-cheap/. Sounds simple but there were a range of very difficult technical challenges to overcome in order to guarantee stability, which ultimately involved the design of custom variable pitch rotors able to provide complete six degrees of freedom at all times. In related news autonomous quadcopters can now navigate small gaps using only on-board processing and a fisheye camera https://www.technologyreview.com/s/603088/watch-this-robotic-quadcopter-fly-aggressively-through-narrow-gaps/.
8. Targeted Ultrasound Microbubbles Open Blood Brain Barrier
Building on work that opens the blood brain barrier with ultrasound and microbubbles, the technique can now target the delivery of drugs just to certain brain regions and without exposing the rest of the body to the circulating drug http://www.agenciasinc.es/en/News/Microbubbles-and-ultrasound-open-the-blood-brain-barrier-to-administer-drugs. Drugs are now incorporated into the lipid-coated microbubbles, which are injected into the patient as before, while the desired region of the brain is targeted with focused ultrasound; the ultrasound causes the bubbles to temporarily open the blood brain barrier only in that region, also causing the drugs to be released only in that region. Experiments in mice and monkeys confirmed the effectiveness.
9. Nanocrystal Night Vision
Advances in nanophotonics have for the first time produced semiconductor nanocrystal antennas on optically transparent substrates http://www.anu.edu.au/news/all-news/anu-invention-to-inspire-new-night-vision-specs. Grown as arrays on a thin film and applied to normal glasses lenses the surface might enable cheap and easy night vision. The structures can be designed to shift the direction, frequency, and polarisation of light passing through the device, and might additionally find application in holography and optical computing.
10. Energy Technologies
A couple of unusual but interesting energy-related technologies this week. First, a new nanoceramic material would constitute safer casings for nuclear reactors, more safely handling liquid metal coolants such as sodium, and instead of becoming brittle over time like many other materials under intense radiation, actually becoming tougher and stronger from the radiation https://www.engr.wisc.edu/new-materials-safe-economical-nuclear-reactors/. Second, leading on from unconventional oil and gas fracking technology and the geological deposits that characterise these sources, there are different (vast) rock deposits embedded with hydrocarbons that cannot be obtained via fracking or any other technology, except for this new microwave technology that was developed that can effectively extract oil and water from these rocks http://www.nextbigfuture.com/2016/12/microwave-oil-recovery-could-unlock.html.
SciTech Tip Jar: http://www.scitechdigest.net/p/donate.html